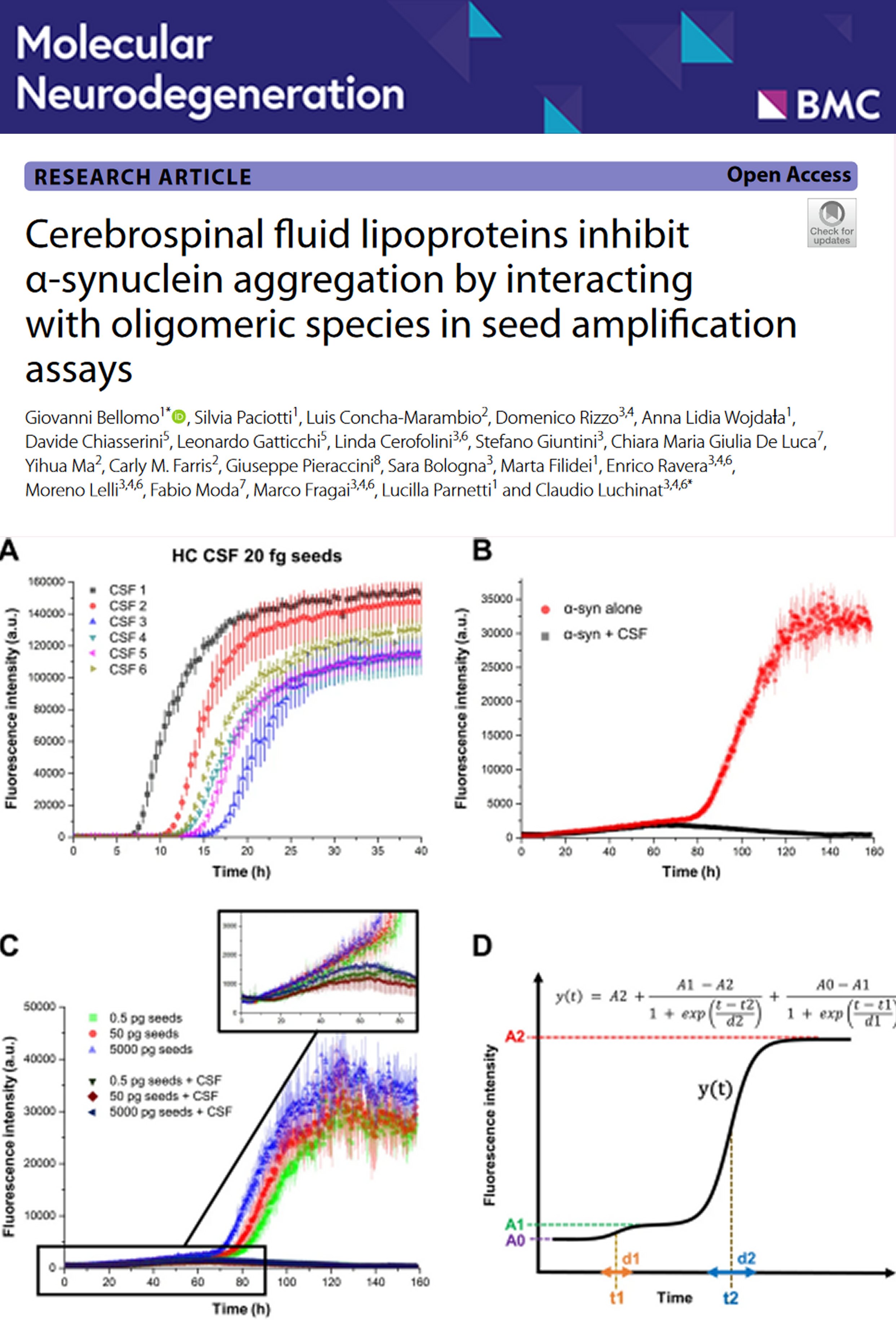
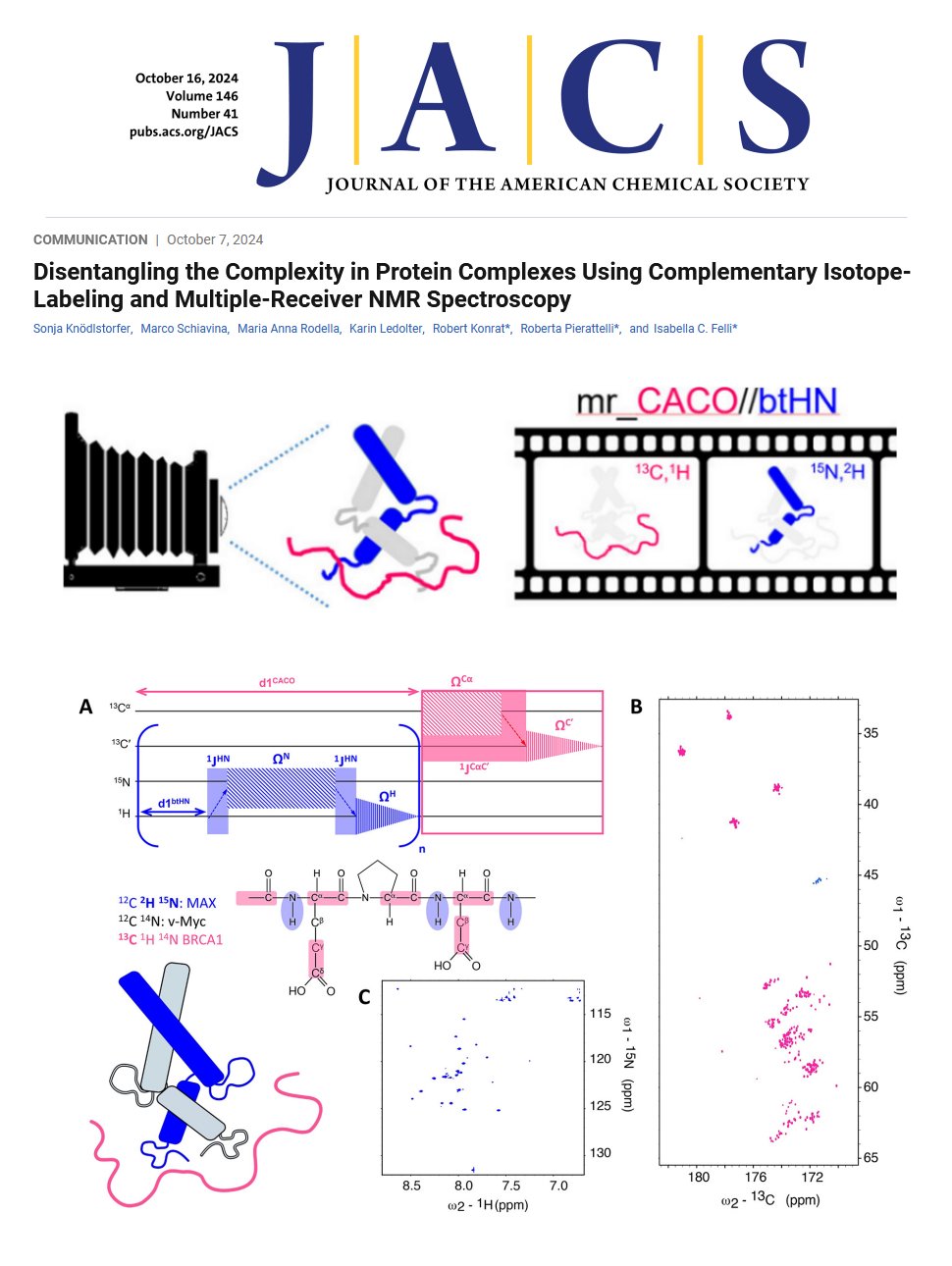
Publications acknowledging the Italian centre of Instruct-ERIC (2025)
Publications acknowledging the Italian centre of Instruct-ERIC (2024)
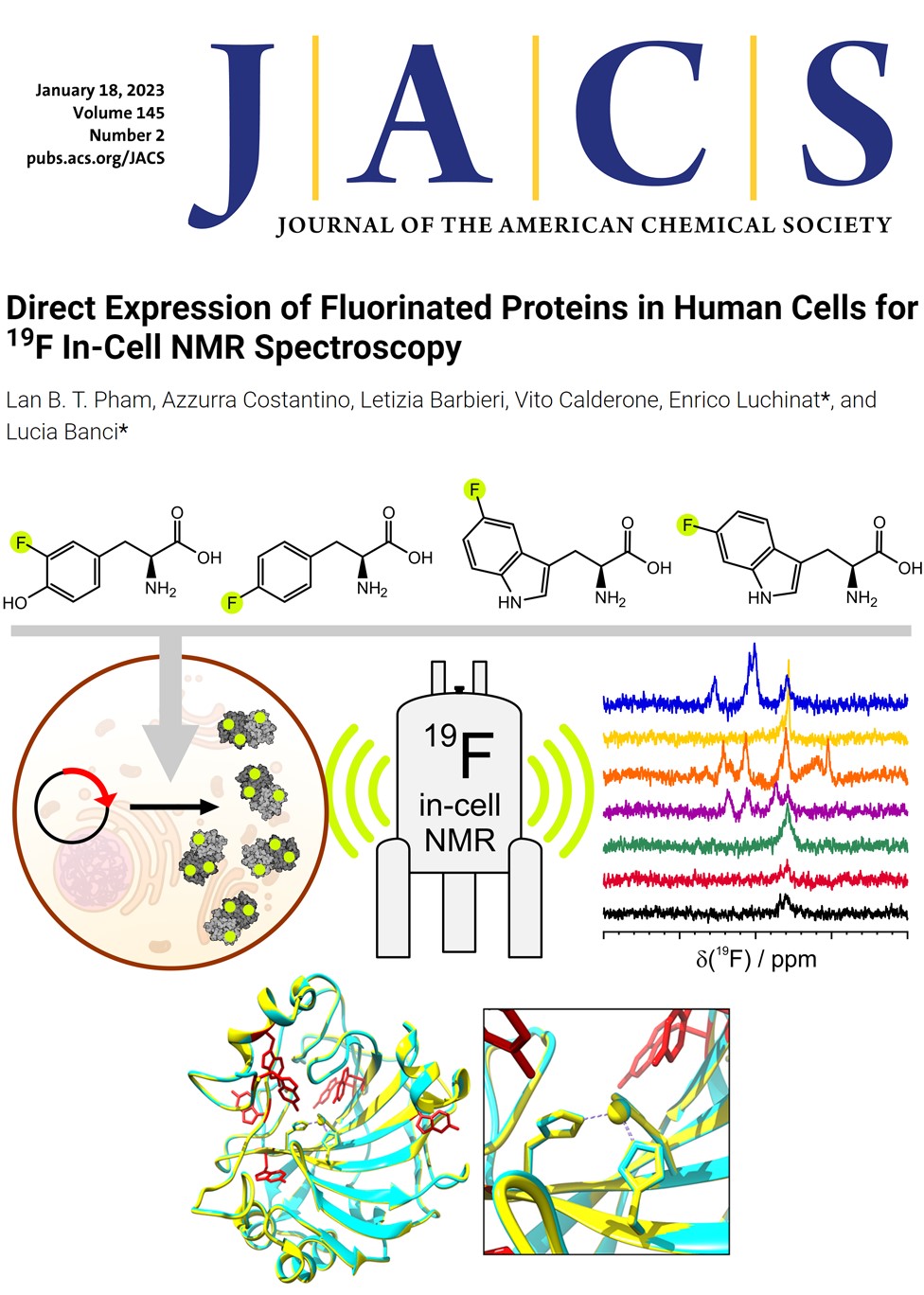
Publications acknowledging the Italian centre of Instruct-ERIC (2022-2023)
Archive of scientific publications since 2010
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 |
Edited Books
C. Luchinat, G. Parigi, E. Ravera Paramagnetism in Experimental Biomolecular NMR, RSC (2018)
Metallomics and the Cell - Metal Ions in Life Sciences Vol. 12, Banci L., Springer, 2013
Books
Bertini, Luchinat, Parigi, Ravera, NMR of Paramagnetic Molecules, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016Bertini, Luchinat, Parigi, Solution NMR of Paramagnetic Molecules, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2001
Bertini, Luchinat, NMR of paramagnetic substances, Elsevier, 1996
Banci, Bertini, Luchinat, Nuclear and electron relaxation, VCH, 1991
Bertini, Luchinat, NMR of Paramagnetic Molecules in Biological Systems, The Benjamin/Cummings Publ. Co. Inc., 1986
Scientific Annual Reports
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 |